
Große Dinge im Geschäftsleben werden nie von einer Person allein erreicht. Sie werden von einem Team erreicht. Wir haben diese dynamische Gruppe von Menschen
Confused about the alphabet soup of display technologies? This article breaks down the differences between TFT, AMOLED, and IPS displays, explaining their strengths and weaknesses to help you determine which display technology is best suited for your needs. Discover the nuances of brightness, color accuracy, power consumption, and viewing angles to make an informed decision for your next device purchase. Stop guessing and start understanding which display wins!

The abbreviation TFT stands for Thin-Film Transistor. It is a type of liquid crystal display (LCD). The most common use of TFT technology is within LCD’s found in monitors and television sets. It is also commonly used in smartphones and smaller handheld devices. TFT technology is considered an improvement over older passive matrix LCD technology. The use of thin-film transistors allows for brighter images and faster response times compared to earlier LCD’s. Because of its versatility, TFT technology is widely used in the industry and accounts for a large percentage of displays on the market.
These TFT displays account for a significant portion of the LCD market. TFT’s are essentially an active-matrix technology, meaning each pixel is controlled by one to four transistors. This allows for quicker response times and better image control, making them suitable for displaying fast-moving content. They’re found everywhere from your car’s dashboard to the screen of your microwave. The thin-film transistor, therefore, is the core component that allows for the image to be displayed.
A TFT LCD display, or Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display, operates on a principle that combines liquid crystal technology with a matrix of tiny transistors. A matrix of tiny transistors is placed behind the liquid crystal layer. These transistors control the flow of electricity to individual pixels. Each pixel in the display has its own transistor, which controls the amount of light passing through that pixel.
This active-matrix system provides much better control over each pixel compared to older passive-matrix LCDs. When electricity to the display is applied to a specific transistor, it causes the liquid crystal to twist or untwist, either blocking or allowing light to pass through. This is how the image is formed. Because TFTs control each pixel individually, they offer better contrast and faster response times than older LCD technologies. However, they still require a backlight to illuminate the display, which can impact power consumption and brightness levels.
AMOLED stands for Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Unlike TFT LCDs, AMOLED displays do not require a backlight. Instead, each pixel in an AMOLED display emits its own light. This is achieved through the use of organic light-emitting diode technology. Specifically, they use organic materials that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This fundamental difference leads to several advantages, including deeper blacks, higher contrast ratios, and potentially lower power consumption, especially when displaying darker colors.
AMOLED displays are often praised for their vibrant colors and excellent contrast. The fact that individual pixels emit their own light also allows for true blacks, as the pixel can simply be turned off. This contrasts sharply with TFT LCD’s that must block a backlight, which can often result in a grayish black. This ability also makes AMOLED displays more power efficient, especially when displaying dark content. As a result, AMOLED screens have become the gold standard for smartphones.
The key differences between AMOLED and TFT displays stem from their fundamental technology. TFT displays rely on a backlight to illuminate the screen and use liquid crystal to block or allow light to pass through individual pixels. In contrast, AMOLED displays use organic materials that emit light when an electric current passes through.
| Besonderheit | TFT-LCD | AMOLED |
|---|---|---|
| Hintergrundbeleuchtung | Erforderlich | Nicht erforderlich |
| Light Emission | Light is blocked or allowed through | Pixel emits its own light |
| Kontrastverhältnis | Untere | Höher |
| Schwarzwerte | Grayish Black | Echtes Schwarz |
| Energieaufnahme | Higher, especially with bright images | Lower, especially with dark images |
| Manufacturing Cost | Im Allgemeinen niedriger | Im Allgemeinen höher |
Because of the differences, AMOLEDs offer superior contrast ratios and true black levels, which significantly impacts image quality. Power consumption is also a key differentiator, with AMOLEDs typically being more power efficient, especially when displaying darker content. However, the inorganic thin-film transistors needed to drive a TFT are generally cheaper to manufacture than the organic light-emitting diode components used in AMOLED’s.
When it comes to image quality, AMOLED displays generally offer a superior experience compared to TFT displays. AMOLED’s ability to produce true blacks and higher contrast ratios leads to more vibrant colors and a more immersive viewing experience. The fact that individual pixels emit light also results in better viewing angles.
While TFT displays have improved significantly over the years, they still require a backlight, which can lead to light bleed and less accurate color reproduction. AMOLED’s superior contrast and color accuracy make them a better choice for tasks that require high image fidelity. However, the perceived image quality also depends on other factors, such as the resolution, brightness, and color calibration of the display. Despite the benefits, AMOLED screens are more prone to burn-in over time, which is something to consider.

When discussing display technologies, IPS (In-Plane Switching) often enters the conversation alongside TFT and AMOLED. IPS is a type of TFT LCD technology that specifically addresses the viewing angle and color reproduction limitations of earlier TFT displays, specifically twisted nematic (TN) panels. Here’s a breakdown:
Therefore, IPS is a specific type of TFT technology designed to improve color accuracy and viewing angle. AMOLED is a fundamentally different technology that offers even greater advantages in terms of contrast, black levels, and power efficiency.
TFT displays offer several advantages that have contributed to their widespread adoption, particularly when using IPS technology. One of the main advantages is their relatively low manufacturing cost compared to AMOLED displays. This makes them an attractive option for budget-conscious manufacturers and consumers.
Advantages of TFT:
Disadvantages of TFT:
Despite their disadvantages, TFT displays still offer a good balance of performance and cost, making them a popular choice for many applications. The improvements achieved with IPS technology have also addressed some of the earlier limitations of TFT displays, such as poor viewing angles. TFT screen are used in a variety of products.
AMOLED displays come with a set of unique advantages and disadvantages. One of the most significant advantages is their superior image quality, characterized by deep blacks, high contrast ratios, and bright and vibrant colors. This is due to the organic materials and active matrix organic technology. This is combined with the fact that each pixel emits its own light.
Advantages of AMOLED:
Disadvantages of AMOLED:
Despite these drawbacks, the superior image quality and power efficiency of AMOLED displays have made them a popular choice for high-end smartphones, tablets, and other devices where display performance is critical. OLEDs are the future for many devices.
The choice between TFT and AMOLED depends heavily on the specific application. For applications where cost is a primary concern, TFT displays are often the better option. TFT LCD is also preferred when durability is important. This is why TFT displays are common in industrial applications or outdoor kiosks.
However, for applications where image quality is paramount, such as high-end smartphones and VR headsets, AMOLED displays are typically the preferred choice. AMOLED’s ability to deliver true blacks and high contrast ratios can significantly enhance the user experience. It is also the best option for applications where power consumption is a major concern. Especially, AMOLED displays perform well in devices with limited battery capacity. Consider your budget, desired image quality, and power requirements when choosing.
Ultimately, the best display technology depends on individual needs and preferences. If you are on a tight budget, TFT displays offer a good balance of performance and cost. If you prioritize image quality and power efficiency, and you are willing to pay a premium, AMOLED displays are generally the better choice.
Consider the following factors:
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the display technology that best meets your specific needs and priorities. The question of which display technology is best really depends on the specific needs and priorities.


Dieser Artikel taucht tief in die faszinierende Welt der Mikrodisplays ein und konzentriert sich insbesondere auf die bahnbrechende 4K-OLED-Technologie, die von Sony Semiconductor Solutions entwickelt wurde.

Dieser Artikel taucht in die Welt der Dünnschichttransistor-LCD-Anzeigemodule (TFT) ein und erkundet ihre Technologie, Vorteile und vielfältigen Anwendungen.

This article dives into the fascinating realm of small OLED displays, exploring their unique characteristics, applications, and the technology that makes them possible.

Dieser Artikel erkundet die faszinierende Welt der LCD-Technologie (Liquid Crystal Display) und konzentriert sich auf die wesentliche Rolle von Treiberplatinen und Controllern für die Funktion dieser Displays.

In diesem Artikel tauchen wir in die Welt der LCD-Bildschirmreparatur ein. Er vermittelt Ihnen ein umfassendes Verständnis der Probleme, die bei einem kaputten oder gesprungenen Bildschirm auftreten können, wie Sie diese erkennen und welche die besten verfügbaren Lösungen sind.
This article explores how to connect an LCD screen to a Raspberry Pi using an HDMI driver board, essentially turning your single-board computer into a miniature HDMI monitor.
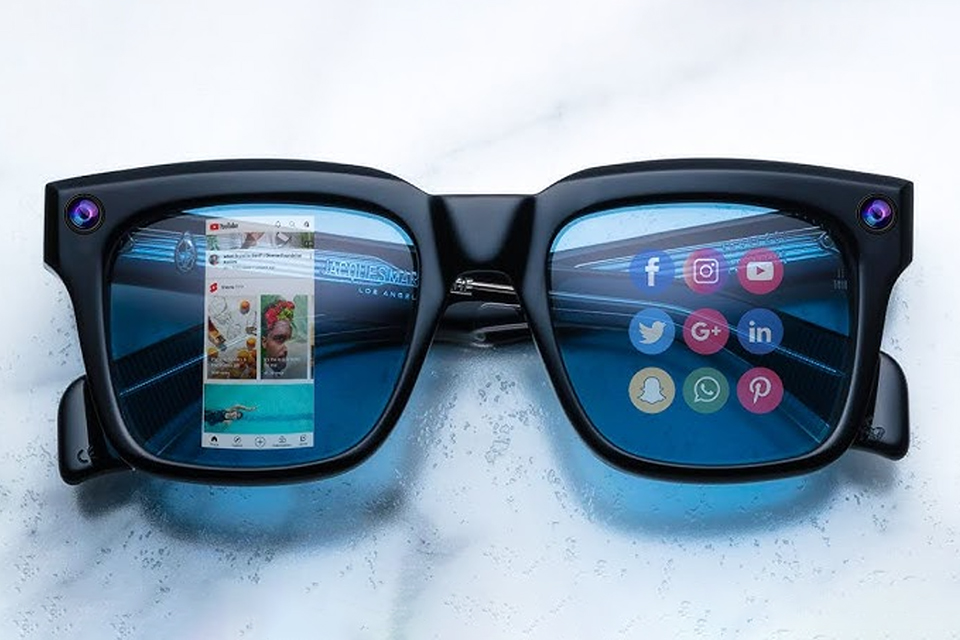

This article dives into the exciting world of augmented reality (ar) lenses, specifically focusing on the development and potential of an interchangeable lens system for ar glasses.

This article dives deep into the lifespan and durability of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays compared to LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens.

@ 2025 Anzeigemodul. Alle Rechte vorbehalten.
Füllen Sie das untenstehende Formular aus und wir werden uns in Kürze mit Ihnen in Verbindung setzen.