
Les grandes choses dans le monde des affaires ne sont jamais le fait d'une seule personne. Elles sont le fait d'une équipe. Nous avons ce groupe dynamique de personnes
This article explores how to connect an LCD écran à un Raspberry Pi using an HDMI carte de conducteur, essentially turning your single-board computer into a miniature HDMI display screen. Whether you’re looking to create a custom afficher for a project, build a portable gaming system, or simply repurpose an old laptop screen, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process. It’s worth reading because it breaks down the technical jargon, offers step-by-step instructions, and highlights potential pitfalls to avoid, empowering even novice users to complete this exciting DIY project.
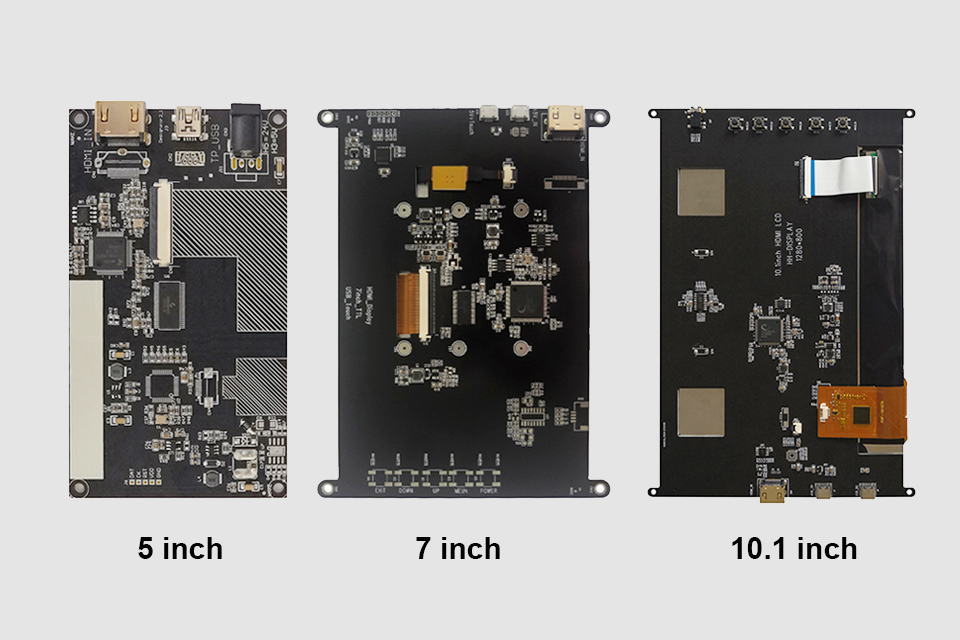
Le Raspberry Pi, a versatile single-board computer, offers a world of possibilities for DIY projects. Connecting it to an HDMI Écran LCD afficher expands these possibilities even further.
Firstly, an HDMI Écran LCD allows you to build embedded systems. Imagine creating a custom control panneau for a smart home, a portable retro gaming console, or a dedicated afficher for sensor data. The compact size and low power consumption of the Raspberry Pi, combined with an Écran LCD écran, make this feasible. Secondly, using an HDMI LCD can be more cost-effective than purchasing a pre-built moniteur. You can often find kits that include the Écran LCD panneau et carte de conducteur at a reasonable price, especially if you’re comfortable with a little assembly.
The three essential components for this project are the Écran LCD panneau, le carte de conducteur, et le HDMI câble. Le Écran LCD panneau is the actual écran d'affichage itself. It requires a carte de conducteur to translate the HDMI signal de la Raspberry Pi into a format the Écran LCD panneau can understand.
Le carte de conducteur is a crucial piece of tech. It takes the digital HDMI input and converts it to the analog signals needed to control the pixels on the Écran LCD écran. It also handles tasks like adjusting brightness, contrast, and color. Finally, the HDMI cable connects le Raspberry Pi au carte de conducteur, transmitting the signal vidéo. Ensure you choose a compatible HDMI câble for optimal signal transmission.
The size of the Écran LCD écran depends entirely on your project requirements. A 7 inch Écran LCD écran est un choix populaire pour Raspberry Pi projects due to its balance of portability and visibility. It’s large enough to display text and graphics clearly, yet small enough to be easily integrated into custom enclosures.
However, you can find Écran LCD écrans in various sizes, from smaller 3.5-inch affiche to larger 10-inch or even larger panneaux. Consider the intended application. For a handheld gaming console, a smaller écran might be preferable. For a desktop écran d'affichage alternative, a larger afficher would be more suitable. Also, think about the resolution. Higher resolution écrans provide sharper images, but they also require more processing power from the Raspberry Pi.
Here’s a table summarizing common LCD screen sizes and their typical applications:
| Taille de l'écran | Applications typiques | Avantages | Inconvénients |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 inch | Small embedded systems, portable displays | Very compact, low power consumption | Small screen real estate, limited resolution |
| 7 inch | Portable gaming consoles, DIY tablets, control panels | Good balance of size and portability, reasonable cost | May be too small for some desktop applications |
| 10 inch | Desktop monitor alternatives, larger embedded systems | Larger screen real estate, better for viewing video | Less portable, higher power consumption |
Sélection du bon carte de conducteur is vital for a successful project. While VGA affiche were common, HDMI is the preferred saisir method for modern Raspberry Pi projects. HDMI provides a higher-quality numérique video signal par rapport à VGA’s analog signal. This results in a sharper, clearer image.
When choosing a carte de conducteur, check for compatibility with your Écran LCD panneau and your Raspberry Pi. Le carte de conducteur must soutien the resolution and interface of your Écran LCD panneau. La plupart Écran LCD kits come with a carte de conducteur specifically designed for the included panneau. Also, ensure the carte de conducteur has the necessary saisir ports, such as HDMI, and that it’s compatible with the Raspberry Pi HDMI output.

When you receive your new HDMI LCD kit, the excitement is palpable. The unboxing process is crucial to ensure that you have all the necessary components and that everything works properly. Typically, an HDMI LCD kit will contain the following:
Before proceeding, check each item carefully for any physical damage. Inspect the Écran LCD écran for scratches or cracks. Ensure all câbles are present and in good condition. A quick visual inspection can prevent headaches later.
Now comes the exciting part: connecting le Écran LCD carte de conducteur à votre Raspberry Pi. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
After 1 step, your Raspberry Pi should automatically detect the HDMI afficher and output video au Écran LCD écran.
Providing adequate pouvoir is crucial for the stability of your HDMI Écran LCD setup. The Écran LCD panneau et le carte de conducteur both require pouvoir, and their pouvoir requirements can vary depending on the size and type of afficher.
Le carte de conducteur typically requires a separate pouvoir supply, often a DC adapter with a specific voltage (e.g., 12V) and amperage (e.g., 2A). Check le caractéristiques de votre carte de conducteur to determine the correct pouvoir requirements. Using an incorrect pouvoir supply can damage the carte de conducteur ou Écran LCD panneau.
Le Raspberry Pi itself also needs pouvoir. While it can sometimes pouvoir smaller affiche through its GPIO pins, it’s generally recommended to utiliser a separate pouvoir approvisionnement pour le Écran LCD to avoid straining the Raspberry Pi pouvoir circuitry.
Sometimes, things don’t go as planned. Here are some common issues and how to fix them:
/boot/config.txt). Détail instructions on how to do this can be found online.Once you have a working HDMI Écran LCD setup, you can explore additional enhancements. Adding touche functionality is a popular option, turning your afficher into a full-fledged écran tactile.
Touch écran functionality typically requires a separate touche carte contrôleur que connects au Écran LCD panneau et le Raspberry Pi. Ces planches often use USB for communication. After physically connecting le touche carte contrôleur, you’ll need to install the appropriate drivers on your Raspberry Pi. There are number of ready to utiliser driver available.

Trouver le bon HDMI Écran LCD trousse ou carte de conducteur can be overwhelming with so many options available. Here’s a guide to help you navigate the purchasing process:
Connecting an HDMI Écran LCD à un Raspberry Pi opens up a world of creative possibilities. By understanding the components involved, following the connection steps carefully, and troubleshooting common issues, you can transform your Raspberry Pi into a versatile HDMI monitor.
10 Important Things to Remember:
Les modules d’affichage OLED, en particulier les variantes OLED graphiques, révolutionnent la façon dont nous interagissons avec les appareils, offrant des visuels nets, des couleurs éclatantes (dans certains cas) et une efficacité énergétique exceptionnelle.

Le module LCD 16×2, pierre angulaire des systèmes embarqués, est un outil fantastique pour afficher des informations textuelles.

This article dives deep into the lifespan and durability of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays compared to LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens.

This article explores how to connect an LCD screen to a Raspberry Pi using an HDMI driver board, essentially turning your single-board computer into a miniature HDMI monitor.

This article dives into the fascinating realm of small OLED displays, exploring their unique characteristics, applications, and the technology that makes them possible.

This article explores how to connect an LCD screen to a Raspberry Pi using an HDMI driver board, essentially turning your single-board computer into a miniature HDMI monitor.

This article dives into the exciting world of augmented reality (ar) lenses, specifically focusing on the development and potential of an interchangeable lens system for ar glasses.

This article dives deep into the lifespan and durability of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays compared to LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens.

@ 2025 display-module. Tous droits réservés.
Remplissez le formulaire ci-dessous et nous vous contacterons sous peu.