
사업에서 위대한 일은 결코 한 사람이 하는 일이 아닙니다. 그것은 사람들의 팀에 의해 이루어집니다. 우리는 역동적인 사람들의 집단을 가지고 있습니다.
이 기사는 세계를 이해하고 탐색하는 데 대한 포괄적인 가이드입니다. LCD 디스플레이 모듈 교체. 깨진 제품을 다루고 있든 화면, 업그레이드 표시하다또는 새로운 프로젝트를 시작하려면 다음이 필요합니다. LCD 화면, 이 가이드는 필요한 지식을 제공합니다. 우리는 다양한 것을 탐구할 것입니다. 유형 ~의 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈, 당신에게 적합한 것을 찾는 과정을 안내해 드립니다. 대사 귀하의 요구 사항에 맞게 답변 호환성, 설치 등에 대한 일반적인 질문. 이 기사는 프로세스의 신비를 풀어주기 때문에 읽어볼 가치가 있습니다. LCD 디스플레이 모듈 교체, 정보에 입각한 결정을 내리고, 수리 비용을 절감하고, 프로젝트에서 최적의 시각적 결과를 얻을 수 있도록 지원합니다. 마지막에는 자신 있게 LCD를 교체하다 다양한 응용 분야에서 찾다 최고 10.1인치 디스플레이 모듈 교체 화면 TFT LCD 귀하의 요구 사항 또는 기타 인치 디스플레이 모듈 교체 화면 TFT 솔루션. 어떤 종류의 솔루션을 탐색해 보겠습니다. 터치스크린 우리가 제공할 수 있는 것은 무엇입니까?

LCD (액정 디스플레이)는 현대 기술에서 널리 사용되기 시작했으며 스마트폰과 노트북부터 산업 장비와 디지털 간판에 이르기까지 모든 것에 등장합니다. 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈, 여러 가지 공통적인 유형 다양한 요구 사항과 응용 프로그램에 맞춰 제공합니다. 탐색 1 가장 인기 있는 옵션 중 하나입니다. 문자 LCD 모듈 영숫자 문자와 기호를 표시하도록 설계되었습니다. 프린터, 복사기, 산업용 제어판과 같이 간단한 텍스트 기반 정보를 표시해야 하는 애플리케이션에서 자주 사용됩니다. 문자 LCD 모듈 일반적으로 16×2(16자)와 같은 표준 구성으로 제공됩니다. 선, 2줄) 또는 20×4.
그래픽 LCD 모듈반면, 텍스트 외에도 이미지와 그래픽을 표시할 수 있습니다. 콘텐츠 측면에서 더 큰 유연성을 제공하며 핸드헬드 게임 장치, 의료 장비, 자동차 대시보드와 같은 애플리케이션에서 일반적으로 발견됩니다. 그래픽 LCD 모듈 128×64 또는 320×240 등 다양한 해상도로 제공됩니다. 픽셀. 터치 스크린 액정표시장치 모듈 통합하다 만지다-사용자가 상호 작용할 수 있는 민감한 계층 표시하다 직접적으로. 두 가지 주요 사항이 있습니다 유형 ~의 만지다 사용되는 기술 LCD 모듈: 저항성과 용량성. 저항성 터치 스크린 압력에 민감하며 스타일러스나 다른 물체로 작동할 수 있는 반면 정전식 터치 스크린 빛에 더 잘 반응한다 만지다 그리고 더 나은 명확성을 제공합니다. 다른 많은 유형 ~의 액정표시장치 모듈 ~이다 사용 가능 시장에는 각각 고유한 기능과 역량이 있는 제품이 있습니다. OLED 디스플레이 더 나은 이미지 품질과 낮은 가격을 제공합니다. 힘 소비하지만 일반적으로 더 비쌉니다. 중요한 에게 메모 그 중 많은 것들이 유형 ~ 할 것이다 맞다 당신의 장치 그러니 자신의 필요와 예산에 맞춰 선택해야 합니다.
올바른 것을 선택하다 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈 귀하의 프로젝트 또는 대사 요구 사항에는 몇 가지 핵심 요소에 대한 신중한 고려가 포함됩니다. 가장 중요한 요소 중 하나는 중요한 요인은 디스플레이의 해상도는 수를 결정합니다. 픽셀 그것은 표시할 수 있고, 결과적으로 이미지의 선명도와 디테일을 표시할 수 있습니다. 복잡한 그래픽이나 많은 양의 텍스트를 표시해야 하는 애플리케이션에는 일반적으로 더 높은 해상도가 선호됩니다. 표시하다 크기 또 다른 중요한 요소입니다. 액정표시장치 모듈 작은 것부터 다양한 크기로 제공됩니다. 디스플레이 웨어러블 기기에서 사용되는 것부터 텔레비전에 사용되는 대형 패널까지. 적절한 크기 의도한 적용 분야와 사용 가능한 공간에 따라 달라집니다.
그만큼 인터페이스 유형 또한이다 중요한 고려하다. 일반적이다 인터페이스 유형 ~을 위한 액정표시장치 모듈 병렬, SPI, I2C 및 LVDS를 포함합니다. 선택 인터페이스 필요한 데이터 전송 속도, 마이크로컨트롤러에서 사용 가능한 핀 수, 배선의 복잡성과 같은 요인에 따라 달라집니다. 고려해야 할 다른 요인에는 다음이 포함됩니다. 시야각, 이는 얼마나 잘 결정되는지 표시하다 다양한 각도에서 볼 수 있습니다. 명도 그리고 대조 표시하다다양한 조명 조건에서 가시성에 영향을 미치며 작동 힘 그리고 온도 범위. 또한 필요한지 생각하는 것도 필수적입니다. 만지다 화면 그리고 그렇다면, 무엇이 유형 ~의 만지다 기술(저항성 또는 용량성)이 귀하의 애플리케이션에 가장 적합합니다. 기억하세요 성냥 당신의 표시하다 기준 치수 당신에게 장치. 이러한 요소를 신중하게 평가하면 다음을 선택할 수 있습니다. 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈 귀하의 특정 요구 사항을 충족하고 귀하의 애플리케이션에서 최적의 성능을 보장합니다. 또한 중요한 에게 성냥 다른 부분품 의 장치 와 함께 표시하다. 그 유형 ~의 커넥터 사용된 것도 고려해야 합니다.
올바른 것을 찾다 교체 LCD 디스플레이 모듈 당신을 위해 장치 또는 프로젝트는 어려워 보일 수 있지만 체계적인 접근 방식을 따르면 프로세스를 단순화하고 호환성을 보장할 수 있습니다. 첫 번째 단계 원본의 사양을 식별하는 것입니다 액정표시장치 표시하다. 이 정보는 종종 다음에서 찾을 수 있습니다. 장치의 사용 설명서, 기술 문서 또는 제조업체 웹사이트에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 중요한 사양 메모 포함하다 표시하다 크기, 해결, 인터페이스 유형, 커넥터 유형, 그리고 모델 번호입니다. 이것은 1 올바른 것을 찾는 첫 단계 부분.
만약 당신이 할 수 없다면 찾다 원본의 정확한 사양 표시하다, 당신은 그것을 조사하여 결정할 수 있습니다 액정표시장치 기준 치수 자체. 라벨이나 표시가 있는지 확인하십시오. 인쇄 회로 기판 또는 뒷면 표시하다 패널. 이 표시에는 다음이 포함될 수 있습니다. 모델 번호 또는 기타 식별 정보. 원래 사양이 있으면 액정표시장치, 호환되는 제품을 검색하기 시작할 수 있습니다. 대사. 온라인 소매업체, 전자 제품 공급업체 및 전문 표시하다 유통업체는 찾아보기에 좋은 곳입니다. 검색할 때는 앞서 식별한 사양을 키워드로 사용하세요. 예를 들어, "대사 액정표시장치 [장치에 대하여 모델]” 또는 “10.1 인치 1280×800 디스플레이 모듈 에스피에이 인터페이스.” 그래야 합니다. 성냥 당신의 장치.
그것은 중요한 잠재적인 사양을 신중하게 비교합니다 대사 액정표시장치 모듈 원본과 함께 표시하다. 주의 깊게 살펴보세요 크기, 해결, 인터페이스 유형, 커넥터 유형, 그리고 핀 구성. 이러한 사양의 작은 차이조차도 비호환성을 초래할 수 있습니다. 특정 사양이 액정표시장치 기준 치수 ~이다 호환 가능, 판매자 또는 제조업체에 연락하여 명확히 하는 것을 고려하십시오. 그들은 추가 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다. 세부 사항 또는 귀하의 특정 사항과의 호환성을 확인하십시오. 장치 또는 프로젝트. 필요한 경우 바꾸다 그만큼 표시하다 항상 찾아보세요 원래의 부분 숫자.
당신이 다음과 같은 상황에 직면하는 것은 드문 일이 아닙니다. 할 수 없다 찾다 정확한 대사 특정한 것에 대해 액정표시장치 화면 또는 디스플레이 모듈. 이는 원래의 이유와 같은 다양한 이유로 발생할 수 있습니다. 표시하다 중단되고 있습니다 장치 너무 나이가 많거나 표시하다 ~이다 관습 설계 쉽게 아니다 사용 가능 시중에 나와 있습니다. 이런 상황에 처해 있다면 절망하지 마세요. 여전히 탐색할 수 있는 몇 가지 옵션이 있습니다.
한 가지 옵션은 호환되는 것을 검색하는 것입니다. 액정표시장치 화면 ~와 함께 비슷한 사양. 정확히 일치하지 않을 수도 있지만 표시하다 같은 것으로 크기, 해상도 및 인터페이스 유형 ~로 작동할 수도 있습니다 대사. 그러나 다음 사항에 세심한 주의를 기울이는 것이 중요합니다. 커넥터 유형 그리고 핀 구성, 약간의 차이도 호환성 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 원본과 잠재적인 데이터시트를 모두 참조해야 할 수도 있습니다. 대사 디스플레이 그들이 있는지 확인하기 위해 호환 가능. 여기에는 약간의 기술적 경험.
또 다른 옵션은 일반 사용을 고려하는 것입니다. 액정표시장치 기준 치수 그리고 그것을 당신에게 맞게 조정합니다 장치 또는 프로젝트. 이 접근 방식은 종종 더 많은 기술적 전문성을 요구합니다. 설계 관습 판자 또는 새로운 회로를 수용하기 위해 기존 회로를 수정합니다. 표시하다. 또한 사용자 정의 펌웨어를 작성하거나 기존 코드를 수정하여 인터페이스해야 할 수도 있습니다. 대사 액정표시장치. 이 옵션은 더 어려울 수 있지만 더 큰 유연성을 제공하고 더 쉽게 사용할 수 있도록 해줍니다. 사용 가능 표시하다 모듈.
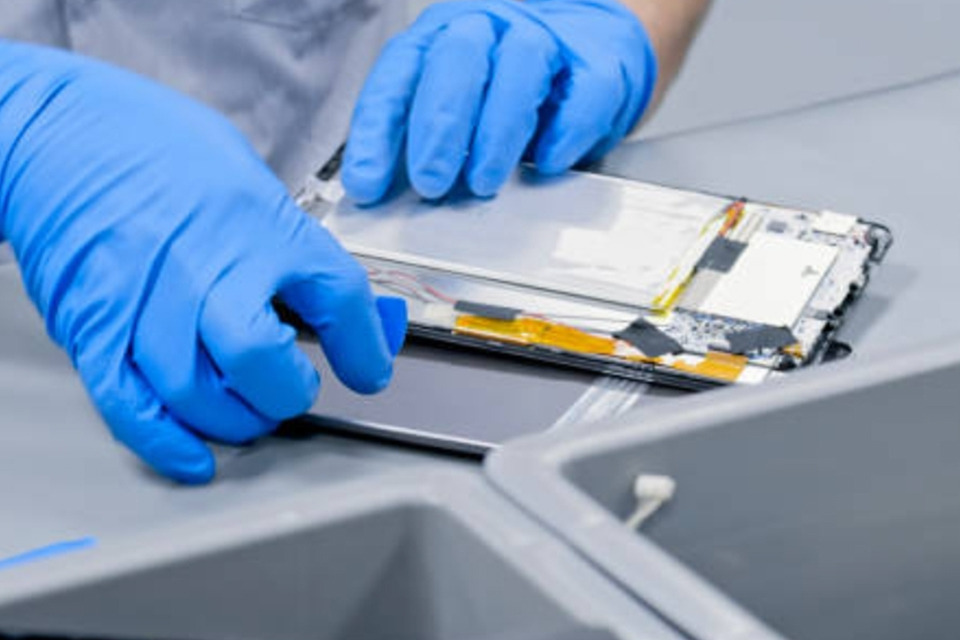
교체 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈 어려운 작업처럼 보일 수 있지만 올바른 도구와 체계적인 접근 방식을 사용하면 관리 가능한 프로세스가 될 수 있습니다. 다음은 이를 수행하는 데 도움이 되는 일반적인 단계별 가이드입니다. 대사 프로세스:
참고하시기 바랍니다 장치의 특정 분해 및 조립 지침에 대한 서비스 매뉴얼 또는 온라인 튜토리얼이 있는 경우 사용 가능. 수행하는 데 편안하지 않은 경우 대사 자신을 위해서 전문가를 찾는 것을 고려하세요 수리하다 서비스입니다. 쉬운 과정은 간단하지만, 어느 정도 기술적인 지식이 필요합니다.
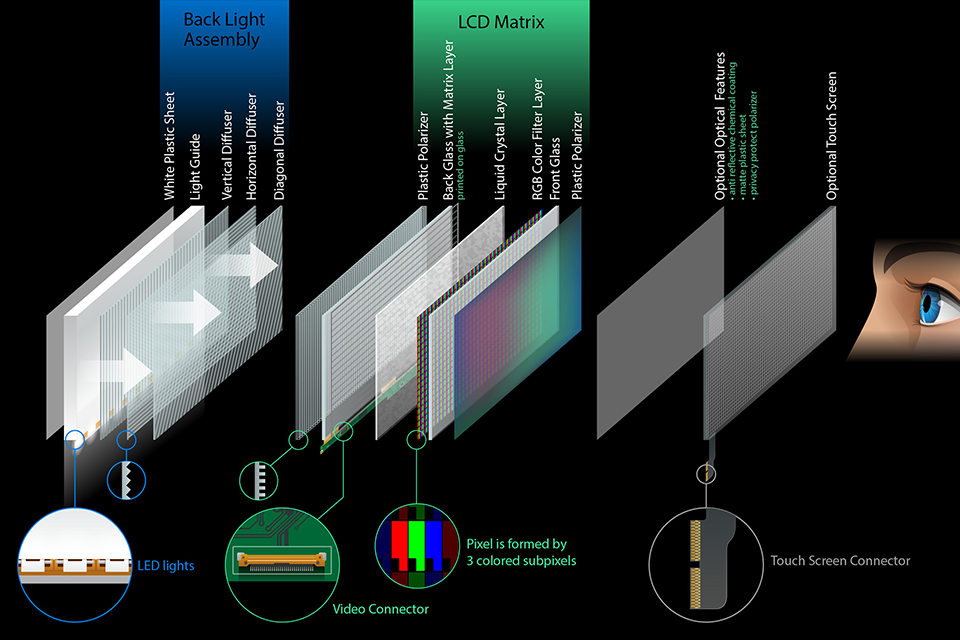
LCD 디스플레이 모듈 메인보드나 마이크로컨트롤러와 인터페이스하기 위해 다양한 유형의 커넥터를 사용합니다. 커넥터 사용은 호환성 및 용이성에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 대사, 그리고 전체적으로 설계 의 장치. 가장 일반적인 몇 가지 사항은 다음과 같습니다. 커넥터 유형 ~을 위한 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈:
| 커넥터 유형 | 설명 | 일반적인 응용 프로그램 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 리본 케이블 커넥터 | 엣지 커넥터가 있는 유연한 케이블로, 종종 특정 디스플레이에 맞게 맞춤 설계됩니다. FPC 및 FFC 커넥터 포함. | 더 작은 액정표시장치 모듈, 모바일 장치, 임베디드 시스템 | 소형, 경량, 유연성 | 깨지기 쉬울 수 있으며 반복 삽입을 위해 ZIF 커넥터가 필요할 수 있으며 사용자 정의 설계로 인해 호환성이 제한될 수 있습니다. |
| 핀 헤더 | 소켓에 삽입되는 금속 핀의 행 인쇄 회로 기판일반적인 피치는 2.54mm와 2.0mm입니다. | 성격 LCD,일부 그래픽 LCD, 개발보드, 취미 프로젝트 | 간단하고 저렴하며 납땜하기 쉽습니다. | 리본 케이블보다 부피가 크고 핀 수가 제한되어 있어 고속 데이터에 적합하지 않을 수 있습니다. |
| ZIF 커넥터 | 잠금 장치(레버 또는 슬라이더)가 있는 커넥터는 다음을 허용합니다. 쉬운 리본 케이블을 손상 없이 삽입하고 제거합니다. | 자주 필요한 장치 표시하다 대사 또는 업그레이드 | 케이블을 보호하고삽입/제거 중 커넥터가 손상되는 것을 방지합니다. 용이하게 한다 쉬운 대사 | 비 ZIF 커넥터에 비해 비용과 복잡성이 증가합니다. |
| LVDS 커넥터 | 트위스트 페어 케이블을 통한 고속 데이터 전송을 위한 차등 신호를 사용하는 커넥터. 종종 표준화됨. | 더 크고 더 높은 해상도 디스플레이 노트북, 모니터, 산업 장비 | 높은 대역폭, 우수한 신호 무결성, 표준화된 커넥터로 호환성 향상 | 간단한 커넥터보다 더 복잡하고 비용이 많이 들며 특정 그래픽 컨트롤러가 필요합니다. |
| eDP 커넥터 | 고해상도용으로 설계된 커넥터 디스플레이, 핀 수 감소, 전력 효율 개선, EMI 감소를 제공합니다. 현대 기기에서 점점 더 많이 사용되고 있습니다. | 노트북, 태블릿, 올인원 컴퓨터, 하이엔드 임베디드 시스템 | 고해상도, 낮은 전력 소모, 감소된 EMI, 더 작은 커넥터 지원 크기 | 더 새로운 기준, 이전 장치나 컨트롤러에서는 지원되지 않을 수 있습니다. |
선택할 때 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈 또는 대사, 세심한 주의를 기울이는 것이 중요합니다. 커넥터 유형 그리고 그것이 맞는지 확인하세요 호환 가능 당신과 함께 장치 또는 마이크로 컨트롤러. 잘못된 것을 사용 커넥터 유형 연결 문제, 신호 무결성 문제 또는 심지어 손상으로 이어질 수 있습니다. 표시하다 또는 다른 구성요소.
교체 후 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈, 몇 가지 일반적인 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 해결할 준비를 하면 시간과 좌절을 줄일 수 있습니다. 다음은 몇 가지 일반적인 문제와 잠재적 해결책입니다.
문제 해결 액정표시장치 표시하다 문제는 종종 제거 과정을 포함합니다. 연결, 설정 및 드라이버를 체계적으로 확인하면 종종 문제를 식별하고 해결할 수 있습니다. 이러한 기본 문제 해결 단계를 시도했지만 여전히 문제가 발생하는 경우 다음을 찾아야 할 때일 수 있습니다. 지원하다 에서 표시하다 제조업체 또는 전문가 수리하다 서비스.
올바른 것을 찾다 교체 LCD 디스플레이 모듈 어디에 있는지 알아야 합니다 가게 그리고 무엇을 찾아야 할지. 여러 유형의 소매업체와 공급업체가 다양한 요구 사항과 전문성 수준에 맞춰 서비스를 제공합니다. Amazon, eBay, AliExpress와 같은 온라인 마켓플레이스는 광범위한 선택을 제공합니다. 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈 다양한 제조업체와 판매자로부터. 이러한 플랫폼은 가격을 비교하고, 고객 리뷰를 읽고, 광범위한 옵션을 찾는 데 편리합니다. 그러나 중요한 제3자 판매자로부터 구매할 때 주의를 기울이고 해당 판매자의 평판과 진위성을 확인하십시오. 제품.
Adafruit, SparkFun 및 Digi-Key와 같은 전문 전자 제품 공급업체는 다음과 같은 우수한 소스입니다. 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈특히 취미인, 제작자, DIY 프로젝트를 진행하는 사람들에게 적합합니다. 이러한 공급업체는 종종 재고를 정리하고 자세한 정보를 제공합니다. 제품 정보 및 데이터시트, 제공 고객 지원하다. 또한 브레이크아웃 보드, 케이블 및 개발과 같은 보완 제품을 제공할 수도 있습니다. 키트 통합 과정을 단순화할 수 있습니다.
산업 등급 또는 특수 등급을 찾는 분들을 위해 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈, 전문화된 표시하다 Mouser Electronics, Arrow Electronics, Future Electronics와 같은 유통업체는 좋은 선택입니다. 이러한 유통업체는 종종 광범위한 디스플레이 특정 애플리케이션이나 산업을 위해 설계된 제품을 포함하여 선도적인 제조업체에서 제공합니다. 또한 다음과 같은 부가가치 서비스를 제공할 수도 있습니다. 관습 표시하다 솔루션, 만지다 화면 통합 및 기술 지원하다.
다음은 다양한 유형의 소매업체와 공급업체를 요약한 표입니다. 교체 LCD 디스플레이 모듈:
| 소매업체/공급업체 유형 | 예시 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 온라인 마켓플레이스 | 아마존, 이베이, 알리익스프레스 | 다양한 선택, 경쟁력 있는 가격, 고객 리뷰 | 판매자 평판이 다양하고 위조 제품의 가능성이 있으며 기술 지원이 제한적입니다. |
| 전자제품 공급업체 | Adafruit, SparkFun, Digi-Key | 큐레이트된 인벤토리, 상세 제품 정보, 좋다 고객 지원하다, 보완 제품 | 온라인 마켓플레이스보다 가격이 높을 수 있으며 특수 또는 산업용 제품은 판매하지 않을 수 있습니다. 디스플레이 |
| 표시하다 유통업체 | 마우저 일렉트로닉스, 애로우 일렉트로닉스, 퓨처 일렉트로닉스 | 다양한 산업용 및 전문용 디스플레이, 부가가치 서비스(예: 관습 솔루션, 만지다 통합), 기술 지원하다 | 가격이 더 높을 수 있으며 최소 주문 수량이 필요할 수 있으며 취미인이나 소량 구매자에게 적합하지 않을 수 있습니다. |
| 제조업체 직접 | 삼성, LG, 샤프 등 | 정품 보장, 최신 모델 및 기술에 대한 접근, 대량 할인 가능성 | 소비자 또는 소량 구매자에게 직접 판매하지 않을 수 있으며 유통업체에 비해 선택 범위가 제한적이며 리드타임이 길어질 수 있습니다. |
쇼핑할 때 교체 LCD 디스플레이 모듈, 그것은 중요한 가격뿐만 아니라 판매자의 평판과 같은 요소도 고려해야 합니다. 유효성 기술 정보 및 지원하다, 그리고 해운 시간. 고객 리뷰를 읽고 다양한 공급업체의 사양을 비교하면 정보에 입각한 결정을 내리는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 찾다 귀하의 요구 사항에 가장 적합한 가치입니다. 또한 연락하다 그만큼 가게 그리고 묻다 그들의 추천에 감사드립니다.
교체하는 동안 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈 종종 DIY 프로젝트가 될 수 있지만 전문가의 도움을 구하는 것이 가장 좋은 상황이 있습니다. 언제 연락하다 에이 수리하다 가게 또는 기술적 지원하다 시간, 돈, 그리고 잠재적인 골치 아픈 일을 절약할 수 있습니다. 전자제품을 다루는 데 익숙하지 않거나 필요한 도구가 부족한 경우 경험일반적으로 전문가의 도움을 받는 것이 좋습니다. 수리하다 종류별로 전문적으로 판매하는 매장 장치 귀하가 작업하는 장비(예: 노트북, 스마트폰, 산업 장비)에는 적절한 진단을 위한 전문성과 장비가 갖춰져 있어야 합니다. 수리하다 표시하다 문제.
전문가의 도움이 필요한 또 다른 상황은 고가치 또는 임무 수행에 중요한 문제를 다루는 경우입니다. 장치. 만약 실수가 발생하면 대사 프로세스로 인해 상당한 재정적 손실, 데이터 손실 또는 안전 위험이 발생할 수 있으므로 신중하게 대처하고 전문가에게 맡기는 것이 가장 좋습니다. 핸들 그만큼 수리하다. 마찬가지로 기본 문제 해결 단계를 시도했지만 여전히 문제를 해결할 수 없는 경우 다음을 수행해야 할 수도 있습니다. 묻다 ~을 위한 지원하다.
많은 장치 그리고 표시하다 제조업체는 기술을 제공합니다 지원하다 전화, 이메일 또는 온라인 채팅과 같은 다양한 채널을 통해. 문제 해결에 대한 지침을 제공할 수 있습니다. 대사 절차 또는 보증 청구. 일부 제조업체는 또한 훈련을 받고 장비를 갖춘 공인 서비스 센터 네트워크를 유지합니다. 수리하다 그들의 제품. 연락하기 전에 수리하다 가게 또는 지원하다, 가능한 한 많은 정보를 수집하세요 장치 그리고 표시하다 문제입니다. 여기에는 다음이 포함됩니다. 장치 모델 숫자, 액정표시장치 표시하다 사양, 세부 사항 문제에 대한 설명과 이미 취한 문제 해결 단계를 알려주세요. 더 많은 정보를 제공할수록 더 빠르게 그리고 더 효과적으로 수리하다 기술자 또는 지원하다 상담원이 도와드릴 수 있습니다.
성공적으로 교체한 후 액정표시장치 디스플레이 모듈, 그것은 중요한 적절한 관리를 통해 장수명과 최적의 성능을 보장해야 합니다. 적절한 관리와 유지관리는 손상을 방지하고 향후 수리 필요성을 줄이는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 유지하다 당신의 표시하다 최고로 보입니다. 가장 중요한 의 측면 액정표시장치 표시하다 관리란 정기적인 청소입니다. 먼지, 지문 및 기타 이물질이 쌓일 수 있습니다. 화면 표면, 가시성에 영향을 미치고 잠재적으로 긁힘을 일으킬 수 있습니다. 깨끗한 당신의 액정표시장치 화면, 부드럽고 보푸라기가 없는 마이크로파이버 천을 사용하십시오. 종이 타월, 티슈 또는 거친 천은 사용하지 마십시오. 이것들은 표시하다. 할 수 있습니다 사용 증류수를 사용하지만 직접 뿌리지 마십시오. 화면.
정기적인 청소 외에도 중요한 에게 핸들 당신의 액정표시장치 표시하다 조심하십시오. 과도한 압력을 가하지 마십시오. 화면 표면이 손상될 수 있으므로 픽셀 또는 기본 레이어. 운송할 때 장치 와 함께 액정표시장치 표시하다노트북이나 휴대용 모니터와 같은 사용 보호하기 위한 패딩 케이스 또는 슬리브 화면 충격과 긁힘으로부터 보호합니다. 액정표시장치 표시하다 와 함께 만지다 화면, 당신이 가지고 있는 물건에 주의하세요 사용 그것과 상호 작용합니다. 대부분의 최신 용량성 만지다 화면 아주 그렇다 튼튼한, 날카롭거나 연마성이 있는 물체를 사용하면 긁힘이나 기타 손상이 발생할 수 있습니다. 정전식 터치펜에 특별히 설계된 손가락이나 스타일러스를 사용하세요. 만지다 화면.
환경 요인은 또한 성능과 수명에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 액정표시장치 표시하다. 노출을 피하십시오 표시하다 극한의 온도, 높은 습도 또는 장시간 직사광선에 노출될 경우 이러한 조건은 손상을 일으킬 수 있습니다. 액정표시장치 패널, 백라이트, 또는 다른 구성 요소. 필요한 경우 사용 당신의 장치 혹독한 환경에서는 해당 목적에 맞게 설계된 보호 케이스나 인클로저를 사용하는 것을 고려하세요.

이러한 주요 요점을 염두에 두고 이 기사에 제공된 지침을 따르면 다음 문제를 해결하는 데 큰 도움이 될 것입니다. LCD 디스플레이 모듈 교체 자신감을 가지고 프로젝트를 진행하세요. 새로운 것을 즐기세요 액정표시장치 표시하다!

This article dives into the fascinating realm of small OLED displays, exploring their unique characteristics, applications, and the technology that makes them possible.

이 글에서는 Arduino와 ESP32와 같은 마이크로컨트롤러와 16×2 LCD 모듈을 인터페이싱하는 방법을 자세히 살펴보며, 특히 I2C 모듈을 사용하지 않고 설정하는 방법에 초점을 맞춥니다.

This article dives deep into the world of 0.96 inch OLED display modules, specifically focusing on the 128×64 resolution variant that communicates via the I2C interface.
이 글에서는 디스플레이 기술의 복잡한 세계를 탐구하며, 특히 OLED와 LCD 디스플레이를 비교합니다.

이 기사에서는 OLED(유기 발광 다이오드) 디스플레이의 수명과 내구성을 LCD(액정 디스플레이) 화면과 비교하여 자세히 살펴봅니다.
사업에서 위대한 일은 결코 한 사람이 하는 일이 아닙니다. 그것은 사람들의 팀에 의해 이루어집니다. 우리는 역동적인 사람들의 집단을 가지고 있습니다.
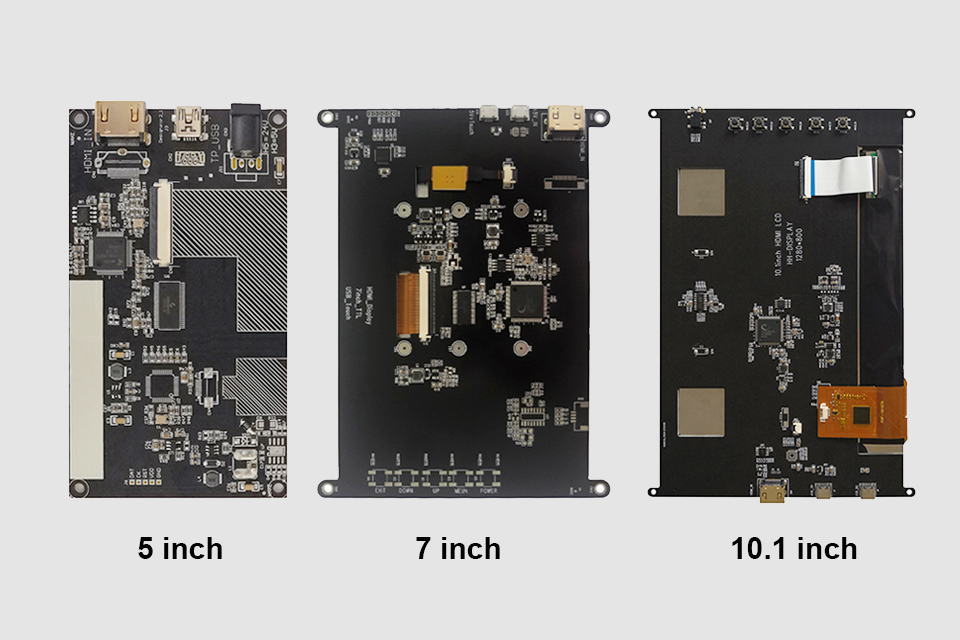
이 문서에서는 HDMI 드라이버 보드를 사용하여 LCD 화면을 Raspberry Pi에 연결하는 방법을 살펴보고, 기본적으로 단일 보드 컴퓨터를 소형 HDMI 모니터로 바꾸는 방법을 설명합니다.
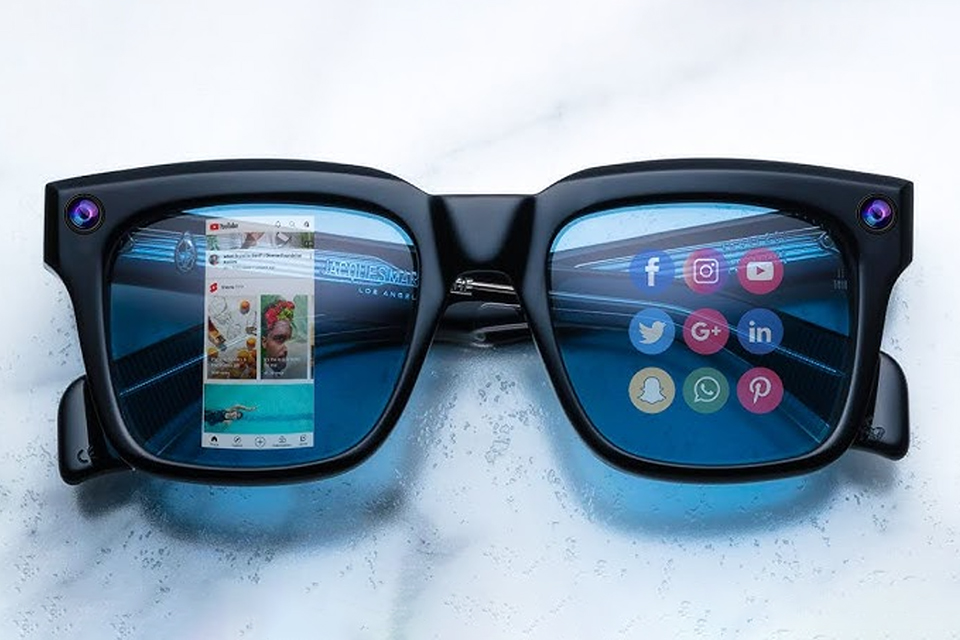

이 기사에서는 증강 현실(AR) 렌즈의 흥미로운 세계를 깊이 있게 살펴보며, 특히 AR 안경용 교환 렌즈 시스템의 개발과 잠재력에 초점을 맞추고 있습니다.

이 기사에서는 OLED(유기 발광 다이오드) 디스플레이의 수명과 내구성을 LCD(액정 디스플레이) 화면과 비교하여 자세히 살펴봅니다.

@ 2025 디스플레이 모듈. 모든 권리 보유.
아래 양식을 작성하시면 곧 연락드리겠습니다.