
Great things in business are never done by one person. They’re done by a team of people. We have that dynamic group of peoples
The world of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is rapidly evolving, and at the heart of this transformation lies a critical component: the display. Micro OLED, a cutting-edge display technology, is poised to redefine the visual experience in head-mounted displays. This article delves into the intricacies of micro OLED displays, their advantages over traditional technologies, and how they are revolutionizing VR and AR. If you’re fascinated by the future of immersive technology and want to understand how micro OLED is driving innovation in display technology, then this is a must-read.

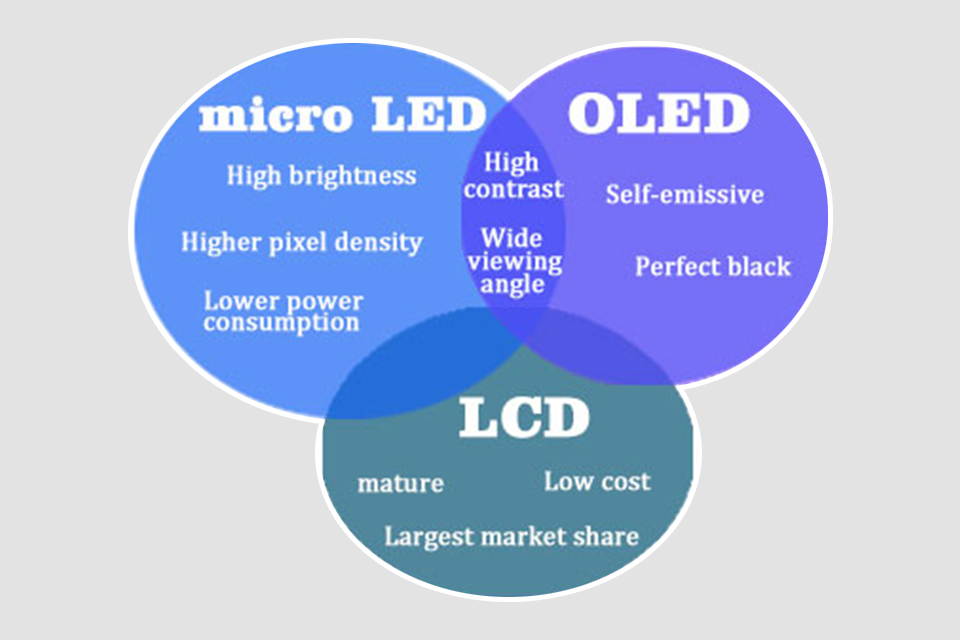
OLED, or Organic Light-Emitting Diode, is a display technology that uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Unlike LCD, which requires a backlight, OLEDs are self-emissive, meaning each individual pixel produces its own light. This feature is what gives OLED displays their high contrast ratio and vibrant colors, making them a popular choice for smartphones, tvs, and other display devices. OLED technology’s ability to produce deep blacks and incredibly bright whites contributes to its high contrast. Since OLEDs don’t need a backlight, they also allow for thinner and more flexible display designs.
The popularity of OLED displays stems from their superior image quality. The self-emissive nature of OLED pixels allows them to be turned off completely, creating true blacks, and therefore a very high contrast. This high contrast, combined with their ability to produce a wide color gamut, results in images that are rich, vibrant, and incredibly detailed. These characteristics make OLEDs ideal for various display applications where image quality is paramount. The fast response times of OLED pixels also make them better suited for high-speed content, reducing motion blur.
A micro OLED display, also known as an OLED microdisplay, takes the fundamental OLED technology and miniaturizes it dramatically. Traditional oled displays are typically fabricated on a glass substrate, while micro oled displays are built on a silicon wafer instead, which allows for extremely small pixel sizes and extremely high pixel density. This shift in substrate is the crucial difference that enables micro OLEDs to achieve the ultra-high resolution necessary for applications like VR and AR. These micro oled displays are specifically designed for small-size display applications.
The key difference lies in the substrate and the manufacturing process. Using a silicon wafer instead of a traditional substrate allows for the creation of much smaller pixels, resulting in significantly higher pixel density. This high pixel density is vital for head-mounted displays where the screen is close to the user’s eyes. The transition to micro oled, therefore, is driven by the need for smaller, more efficient displays that deliver ultra-high resolution and sharper images, which are not typically achievable with traditional oled displays. Essentially, a micro oled is a type of oled designed for use in a very small form factor.
The high pixel density and small size of micro oled display technology makes them exceptionally well-suited for vr and ar applications. In these immersive experiences, the display is very close to the eye. If the display lacks sufficient pixel density, the viewer will perceive the individual pixels and the image will appear grainy or blurry, breaking the immersive experience. Micro oleds can achieve significantly higher pixels per inch (ppi) which results in sharper, clearer images, and makes the virtual or augmented world appear more realistic.
Furthermore, the high contrast ratio of micro oled displays enhances depth and clarity, making virtual and augmented scenes look more believable. The fast response times of oled pixels also reduce motion blur which is critical for VR applications where users are constantly moving, and changes on screen need to be immediate and smooth. These attributes, combined with their small size and low power consumption, make micro oleds a key technology for enhancing the overall vr and ar experience. The micro oled display allows for the creation of much smaller and lighter vr headset, improving user comfort.
When comparing micro oled technology to other display technologies, such as lcd, the differences are significant, especially when considering the needs of vr and ar headsets. LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) use a backlight and color filter which means they cannot achieve the same contrast ratio as oleds since they cannot turn off individual pixels completely. This results in lower contrast and less vivid colors compared to oled displays. In a side by side comparison, especially in displaying black color, the oled will perform much better.
Micro oled display offers a superior image quality in a much smaller form factor. LCD displays, while they are a popular display technology for many consumer products, like laptop screens, and tvs, cannot achieve the level of pixel density or contrast ratio as micro oled. Additionally, LCDs tend to have slower response times, leading to more noticeable motion blur, which is a particular issue in VR where fast motion is common. For displays that need to be high resolution, and high contrast, the micro oleds are worth prioritizing over lcd technology. The technology used in oled also generally allows for a wider color gamut than typical lcd displays.
The key advantage of using micro oled in head-mounted displays is the combination of small size, ultra-high resolution, and high image quality. These micro oled displays are constructed on a silicon wafer which allows the individual pixels to be much smaller, and packed much tighter together, compared to traditional oled displays, giving much higher pixel density and a much clearer picture. The ultra-high resolution is necessary for vr and ar applications where the display is placed very close to the eyes, otherwise the individual pixels become visible which detracts from the immersive experience.
Secondly, micro oled displays deliver excellent brightness and high contrast. This is crucial for creating realistic and immersive virtual or augmented environments, especially in bright lighting conditions. The ability of oled pixels to emit their own light results in a high contrast ratio, deep blacks and vibrant colors, significantly improving image quality. Further, the fast response times of micro oleds minimize motion blur, ensuring smooth and clear visuals, which enhances the overall vr and ar experience. These features makes them ideal for head-mounted displays, which need to be high performing, while small and lightweight.
Sony is a major player in the micro oled market, largely thanks to the expertise of the Sony Semiconductor Solutions Group. They have been developing and refining micro oled technology, and have been pushing the boundaries of what is possible with it. Sony has also been investing heavily into micro oled displays for use in vr headsets. Their experience in electronic viewfinders in professional video equipment has been instrumental in their mastery of high-resolution microdisplays, and they have been able to leverage this expertise to produce some of the highest performing micro oleds currently available.
Sony’s focus on high image quality and pixel density makes them a key supplier of micro oled displays for premium vr headsets. Sony’s products often feature two micro oled screens, each dedicated to one eye, ensuring an incredibly immersive and detailed visual experience. In addition, the sony semiconductor solutions group is leading the charge in producing the displays with higher brightness levels, something that is critical in making vr and ar experiences more believable, and accessible even in bright environments. Sony is helping to push micro oled technology to new heights and expand its applications.
Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (ppi), has a profound impact on the image quality of micro oled displays. Higher pixel density means that more pixels are packed into the same display area. With a higher pixel density, the individual pixels become less visible and the image becomes sharper, more detailed and realistic. For vr and ar applications, where the display is very close to the eye, the importance of pixel density is even more significant. If the pixel density is too low, the user will perceive the individual pixels rather than the image, which can cause eye strain and lessen the immersion.
Micro oled displays can achieve exceptionally high pixel densities due to their design on silicon substrate. For comparison, the pixel density of the iPhone’s display is around 450 ppi. Micro oled displays used in head-mounted devices can reach significantly higher pixel densities. Micro oleds used in high-end vr headsets can achieve over 3000 ppi. In some cases micro oleds can reach times the pixel density of a standard mobile phone display, resulting in a much clearer and more seamless viewing experience in vr and ar applications. The ability to pack many more pixels into a smaller space is what sets the micro oled technology apart, and makes them ideal for use in ar and vr headsets.
Manufacturing micro oled displays presents several unique challenges, primarily due to their incredibly small size and high precision requirements. Producing oleds on a silicon substrate requires specialized semiconductor manufacturing processes. Creating extremely uniform thin layers of organic material on a silicon wafer is also a difficult and complex process. Any slight defects in these layers can cause a noticeable difference in brightness or color uniformity, which is particularly visible in a high-resolution micro oled screen. Maintaining consistent quality across all displays is another major challenge.
Further, the semiconductor industry is subject to extremely high precision demands. The oled silicon wafer needs to be produced in a cleanroom environment with precise control of temperature and humidity. Also, due to high density of organic light emitting diodes, the micro oleds are extremely sensitive to contaminations. The process of achieving extremely small pixel pitch, and individual pixels with very high performance, involves many challenging engineering and manufacturing steps. All these steps have to be tightly controlled. The high precision and low tolerances also make micro oleds more expensive to produce compared to traditional oleds.
Micro oled technology significantly enhances the vr and ar experience across various applications. In virtual reality, where an immersive experience is paramount, micro oled displays can provide ultra-high resolution and a high contrast ratio, making virtual worlds appear more detailed and realistic. Whether it’s gaming, virtual tourism, or training simulations, the ability of micro oleds to deliver a high fidelity visual experience makes them indispensable. Micro oled display technology improves the vr experience to new levels.
In augmented reality, micro oleds allow for high brightness and high resolution, ensuring the overlaid digital content is crisp and easily viewable, even in bright daylight conditions. For applications like industrial AR, where technicians need precise digital instructions overlaid onto the real world, micro oleds can provide the necessary clarity and detail for seamless interactions. Micro oleds also enable smaller and lighter ar and vr headsets, enhancing user comfort and practicality. Micro oleds are pushing both the ar and vr applications to new levels, and enable them to be more widely adopted. The potential of vr and ar applications is limitless.
The future of micro oled technology is incredibly promising, with continuous advancements expected in several key areas. We can expect to see further increases in pixel density, leading to even sharper and more detailed images in vr and ar headsets. New manufacturing techniques and material innovations will help bring down the production costs, making micro oleds more accessible for more consumer products. Additionally, future micro oleds may feature even higher brightness levels, wider color gamut, and faster refresh rates.
As semiconductor and display technology matures further, we may also see the integration of new features, such as integrated eye tracking or varifocal capabilities, which will further enhance the vr and ar experience. The high emission efficiency and longer life of micro oled pixels are also very important for the future. With the technology maturing rapidly, the micro oled technology will be more widespread and will find its way into more consumer products, potentially becoming a popular display technology used across various applications. It is likely that the micro oled will not just be limited to vr and ar applications.


This article delves into the fascinating world of display modules, specifically focusing on LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) technology.

This article dives deep into the lifespan and durability of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays compared to LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens.

AMOLED display modules are rapidly becoming the gold standard in visual technology, offering unparalleled image quality, vibrant colors, and exceptional energy efficiency.

The world of displays is constantly evolving, and two technologies consistently dominate the high-end market: AMOLED and OLED.

The world of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is rapidly evolving, and at the heart of this transformation lies a critical component: the display.
This article explores how to connect an LCD screen to a Raspberry Pi using an HDMI driver board, essentially turning your single-board computer into a miniature HDMI monitor.

This article dives into the exciting world of augmented reality (ar) lenses, specifically focusing on the development and potential of an interchangeable lens system for ar glasses.

This article dives deep into the lifespan and durability of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays compared to LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens.

@ 2025 display-module. All right reserved.
Fill out the form below, and we will be in touch shortly.